Lipoma Removal Slow-growing fatty lumps are called lipomas and are usually between the skin and muscle. A doughy, non-tender lipoma moves with slight finger pressure. Lipomas commonly appear in middle age. Some people have several lipomas.
Most lipomas are harmless. Most lipomas don’t need treatment, but if they’re uncomfortable or developing, they may need to be removed. Everyone can get lipomas, however, they usually appear in maturity and peak in middle life. They affect both sexes equally, however, women have more solitary lipomas and males have more numerous ones.
The cause of lipomas is uncertain. Many lipoma patients have a family history of the tumours, suggesting genetic involvement. Lipomas can develop after a blunt injury.
Lipoma Removal Overview
About Lipoma Removal
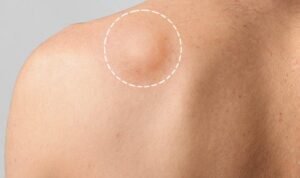
A benign fatty skin bump called a lipoma. Fatty lumps exist between the skin and muscle. These lumps usually grow slowly and don’t hurt. However, a lipoma atop the blood vessels can compress them when it grows. Lipomas can cause pain and discomfort.
Treatment -Diagnosis
Most lipomas are diagnosed by physical exam. The lump’s visibility makes it easier to feel and check. Because of its fatty tissues, lipoma moves when touched. Doctors may do a biopsy to rule out cancer. In addition, ultrasonography, MRI, and CT scans are used to diagnose lipoma.
Procedure
The best lipoma treatment is surgery. The doctor creates a tiny incision and utilises liposuction to remove fat. It is minimally invasive, scarless, and minimises lipoma recurrence. Our skilled surgeons perform the surgery, which is more successful than non-surgical methods.
Lipoma Removal
A lipoma is a subcutaneous fatty mass. Soft and springy, lipomas move easily when touched. Most lipomas aren’t unpleasant or unhealthy, therefore they rarely need treatment. Your doctor can remove a bothersome lipoma.
What is Lipoma Removal?
A round or oval lump of tissue forms beneath the skin as a lipoma. It’s plump, moves smoothly, and rarely hurts. Most often found on the back, trunk, arms, shoulders, and neck, lipomas can appear anywhere. Soft tissue lipomas are benign. Slow-growing, noncancerous. Treatment is unnecessary for most lipomas. Outpatient lipoma removal is available from your doctor.
How common is Lipoma Removal?
Lipomas are prevalent. About 1 in 1,000 people have lipomas. Lipomas can form at any age, but they are most common between 40 and 60. They may be present at birth. All genders get lipomas, but women have them more often.
Learn more about Oily Skin Care Tips at Home
Symptoms Cause for Lipoma Removal
What are lipoma symptoms?
- Lipomas rarely hurt, however, nerve or joint pressure can be irritating. Many lipomas go unnoticed. Lipomas usually:
- Encapsulated particles don’t spread to adjacent tissues.
- Lipomas can be painless or painful depending on their location, size, and blood vessels.
- Round or oval: Rubbery tissue fat lumps are frequently symmetrical.
- They move when touched beneath the skin.
- Smaller than 2 inches: Some lipomas are greater than 6 inches.
Lipomas grow where?
The body can grow lipomas anywhere. Muscles, organs, and brains rarely develop lipomas. Most persons with lipomas have one, although they can increase. Most lipomas form under the skin on:
- Legs or arms.
- Back.
- Neck.
- Shoulders.
- Chest/torso.
- Forehead.
What causes lipomas?
Liposomas’ aetiology is unknown to doctors. Their inheritance is through families. A family member with a lipoma increases your risk. Multiple lipomas can result from certain causes. These conditions cause lipoma:
Dercum’s disease: This rare disorder causes painful lipomas on the arms, legs, and trunk. Also called Anders’ syndrome or adiposis dolorosa. Gardner syndrome: A kind of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), Gardner syndrome causes lipomas and other health issues. Family-inherited multiple lipomatoses are hereditary.
The most common cause of Madelung’s disease is excessive alcohol use in men. Madelung’s illness, also known as multiple symmetric lipomatosis, causes neck and shoulder lipomas.
How are lipomas diagnosed?
Physical exams frequently detect lipomas. Your doctor will touch the lipoma and ask if it hurts. A biopsy may be needed to rule out malignancy in the lipoma. Your doctor sends a lipoma sample to a lab for testing during this operation.These are often mistaken for cysts. Your doctor may arrange an ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan to see this lump. These imaging studies help your doctor distinguish a lipoma from a cyst. If the lipoma has blood vessels and presses against nerves or other tissues, it can aid locate and measure its depth.
The varieties of lipomas?
- All lipomas are fat. Lipomas may contain blood vessels or other tissues. Different forms of lipomas include:
- Fat and blood vessels make up angiolipoma. Angiolipomas hurt.
- White fat cells make up conventional lipomas, the most prevalent form. Energy is stored in white fat.
- Fat and fibrous tissue make up fibrolipoma.
- Hibernoma: Brown-fat lipoma. Other lipomas are mostly white fat. Brown fat cells regulate body temperature by generating heat.
- Myelolipoma: A lipoma with fat and blood-cell-producing components.
- Spindle cell: These lipomas have longer thin fat cells.
- Pleomorphic lipomas have different-sized fat cells.
- Management and Treatment
Treatment for lipomas?
Treatment is unnecessary for most lipomas. Your doctor can surgically remove a bothersome lipoma. You can usually go home the same day after safe and effective lipoma removal. Instead of surgery, your doctor may offer liposuction. Your doctor removes growth fat with a long, thin needle.
Learn more about Monsoon Skin Care Tips
Prevention of Lipoma Removal
Can I avoid lipomas?
Lipomas and related disorders are inherited. It’s impossible to prevent them because they’re inherited. Reduce your alcohol intake to minimise your chance of Madelung’s illness, which causes lipomas.
Lipomas’ prognosis?
Many people have lipomas without noticing them. Most lipomas don’t need treatment, although providers can remove them. Most lipomas don’t return after therapy, but one may grow elsewhere.
Living With
When should I see a doctor regarding lipomas? See your doctor for skin growths, lumps, or knots. Evaluation is necessary to rule out dangerous disorders like liposarcoma. Liposarcoma symptoms resemble lipomas. See your doctor if you experience unexpected pain or other changes in your lipoma. If it grows swiftly (weeks), feels firm, or doesn’t move easily, call your provider. Your doctor will check the lipoma for blood vessels, which indicates an angiolipoma, a rare, painful kind. Millions have lipomas. Though irritating and unattractive, they rarely cause problems. Treatment is unnecessary for most lipomas. See a doctor if a lipoma hurts or makes you worried about its size or placement. You can usually remove lipomas as an outpatient, so you can go home the same day. Removal of lipomas rarely causes regrowth.
A lipoma?
Fat lumps in soft tissues are called lipomas. It’s a tumour but usually harmless. This is the most frequent subcutaneous tumour. About 1 in 1,000 will acquire one. You usually find them in your arms, thighs, or upper body.
Learn more about Tips for Skin Care in Summer
Lipoma symptoms
Small, soft bumps are typical. These are usually under 2 inches broad. You can have multiple. Pressing on the lipoma may feel doughy. Finger pressure moves it easily. Usually painless, they can harm if they hit nerves or blood vessels.
Causes of Lipoma
Not sure what causes them. Middle-aged men and women get them more. They run in families. Researchers don’t know what causes lipomas, but they commonly appear after an injury. Hereditary disorders can cause them. An uncommon disorder called Madelung’s disease can cause them. Mediterranean-ancestry men with alcoholism are especially at risk.
Call a Doctor When
If you have a bump or swelling, see a doctor. They can determine if it’s a harmless lipoma or something more serious. Body organs and muscles can generate lipomas, but rarely. One that hurts or affects your muscles may need to be removed.A lump may be a rare liposarcoma, which grows quickly and hurts. Your doctor may order extra testing if they suspect this.
Learn more about Ayurvedic Health Tips
Lipoma Diagnosis
Lipomas are mainly diagnosed by physical exam. A biopsy, in which a small sample of tissue is taken and examined under a microscope, may confirm the diagnosis. X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs can also clarify.
Remove and Treat Lipomas
Doctors rarely treat lipomas because they’re harmless. It may need monitoring between visits. You may wish to remove one if it aches or looks bad. Your doctor can remove it surgically with a little cut. An injection will numb the area to reduce pain. You should be able to leave. A few sutures may need to be removed in a few weeks. Alternative therapies include Steroids to reduce tumours.
Learn more about Benefits of Pineapple for Men
Large Lipomas
- Giant lipomas are over 2 inches. They can induce nerve pain, self-consciousness, and clothing fit issues.
- These are harder to remove. Doctors may prescribe sleep medication to help you sleep during the surgery. You’ll need a ride home.
- Once removed, lipomas seldom return. Having one doesn’t increase your risk of other ailments.
- Lipomas are lumps under the skin caused by fat cell proliferation.
- However, a lipoma that causes pain, problems, or other symptoms may be removed. The cosmetic look of lipomas also worries some.
Lipomas can form anywhere fat cells are present, however, they usually arise on the shoulders, chest, trunk, neck, thighs, and armpits. In rare situations, they might occur in bones, muscles, or internal organs.
Lipomas are delicate and may migrate under the skin when pressed. They grow slowly over months or years to 2–3 Trusted Sources. Sometimes persons have 10 cm-plus lipomasTrusted Source.
This page discusses lipoma causes, symptoms, and health effects. Risk factors, diagnosis, and removal are covered. Some parents pass on defective genes that produce lipomas. This rare condition is familial multiple lipomatosis.
Learn more about Bridal Skin Care Tips
Certain medical disorders can increase lipomas:
- Gardner’s syndrome
- Cowden’s syndrome
- Madelung disorder
- painful adiposis
Symptoms
A soft, oval-shaped bump under the skin is indicative of a lipoma. Lipomas rarely hurt until they impact joints, organs, nerves, or blood vessels. They rarely induce other symptoms. Deep-skin lipomas may not be visible or palpable. However, a deep lipoma may push on organs or nerves and cause discomfort. Lipomas around the colon can cause nausea, vomiting, and constipation.
Learn more about Teen Skin Care Tips
Effects on health
Fat cells form benign lipomas. However, doctors vary on whether lipomas can become malignant. Liposarcoma is fat cell cancer. According to research trusted Source, many doctors believe liposarcomas are not lipomas but separate tumours. They think clinicians misdiagnose liposarcomas as lipomas. Other scientists believe that lipomas may include malignant and pre-cancerous cells, but they seldom turn cancerous.
